The Eclim Daemon¶
Headless eclipse server¶
The most mature usage scenario that eclim provides, is the running of a headless eclipse server and communicating with that server inside of vim. Starting and stopping of the headless eclipse instance is detailed below.
Starting eclimd
To start eclimd from linux, simply execute the eclimd script found in your eclipse root directory ($ECLIPSE_HOME/eclimd) or the path indicated at the end of the command line installer process.
Note
When starting the eclim daemon, you must start it as the same user who will be running vim.
Note
Even though an eclipse gui is not started in eclim’s headless mode, eclipse still requires a running X server to function. To run eclimd on a truely headless server, please see the headless guide.
Stopping eclimd
To cleanly shutdown eclim use any one of the following.
From Vim:
:ShutdownEclimFrom a console:
$ $ECLIPSE_HOME/eclim -command shutdownLastly you can use Ctrl-C at the console if you are running eclimd in the foreground, or issue a kill to the eclimd java process.
$ kill *pid*You will need to kill the java process since killing the eclimd or eclipse process will not do so. While eclim provides a shutdown hook to support a clean shutdown when the java process is killed in this manner, it is still recommended that you utilize one of the first two methods instead, and reserve this as a last resort. Also note that when killing the java process eclipse will pop up an alert dialog notifying you that the java process was terminated underneath it. This is nothing to be alarmed about.
Headed eclipse server¶
For users that find themselves periodically needing the eclipse gui, or otherwise wanting to keep the gui open while using eclim, there is support for running the eclim server inside of a headed eclipse instance.
Starting eclimd
The eclim daemon inside of eclipse is implemented as an eclipse view which can be found via:
The view will be opened in a new tab in the same pane as the “Problems” tab, as shown below.
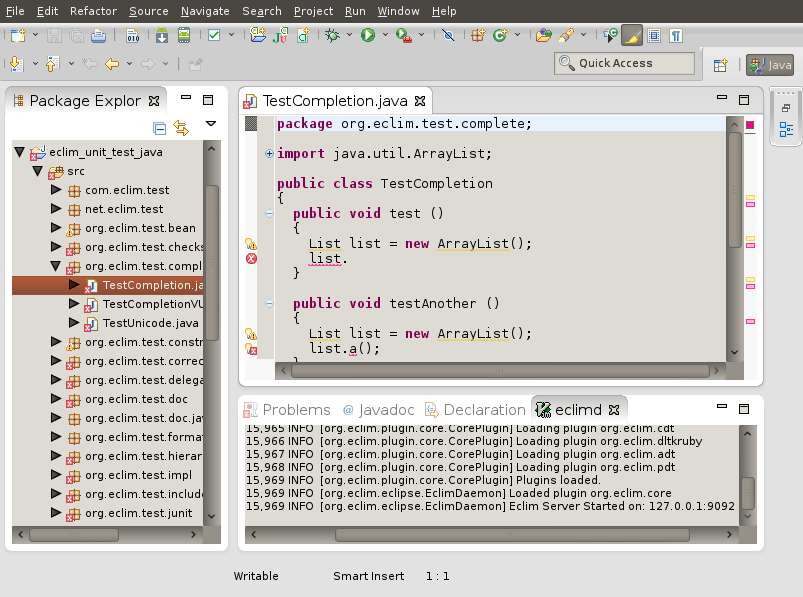
Stopping eclimd
As long as the eclimd tab is open then the eclim daemon will be running. Stopping the eclim daemon is just a matter of closing the eclimd tab. Also note that leaving the tab open and closing eclipse will shutdown the daemon as well, and on the next start of eclipse the tab will be opened, but the eclim daemon will not start until the tab is forced to display itself. In other words, the daemon will not start until the eclimd tab is the active tab in that group.
~/.eclimrc¶
On unix platforms (linux, mac, bsd) eclim supports an optional .eclimrc file located in your home directory. In this file you may supply any system properties or vm args which you would like passed to eclimd at startup. The format of this file is the same as the standard java properties file format with the exception of any vm args which you would like to include.
Ex.
# Bind eclimd to all interfaces
nailgun.server.host=0.0.0.0
# Specifies the port that nailgun / eclimd listens on for client requests.
nailgun.server.port=10012
# Specifies the workspace directory to use
# See $ECLIPSE_HOME/configuration/config.ini for other osgi properties.
osgi.instance.area.default=@user.home/myworkspace
# increase heap size
-Xmx256M
The eclim client will also utilize this file, but only to determine the nailgun server port should you choose to change the default.
Note
Your system must have perl and sed available so that eclim can process your .eclimrc file.
Both the eclim and eclimd scripts also support a -f argument allowing you to specify an alternate location for your .eclimrc:
$ eclimd -f ~/.my_eclimrc
$ eclim -f ~/.my_eclimrc -command ping
eclimd logging¶
Eclimd utilizes log4j for all of its logging. As such, the logging can be configured via the $ECLIPSE_HOME/plugins/org.eclim_version/log4j.xml file.
By default, eclimd writes all logging info to both the console and to a log file in your workspace: <workspace>/eclimd.log
Multiple Workspaces¶
Running eclim against more than one eclipse workspace can be accomplished by running multiple eclimd instances. You must configure each instance to run nailgun on a unique port and supply the path to the workspace you which that instance to use. Once your eclimd instances are up and running the vim client will automatically determine which server to send requests to based on your context. In some cases you may be prompted for which workspace to use if one cannot be determined for you.
Below are some different ways in which you can configure your eclimd instances:
Supply the nailgun port and eclipse workspace path when starting eclimd:
$ eclimd -Dosgi.instance.area.default=@user.home/workspace1 -Dnailgun.server.port=9091 $ eclimd -Dosgi.instance.area.default=@user.home/workspace2 -Dnailgun.server.port=9092
If you are using the eclimd view in the eclipse gui, then you can start the eclipse gui with the desired nailgun server port (note that you must place the -vmargs option before the list of jvm arguments):
$ eclipse -vmargs -Dnailgun.server.port=9092
Specify the port and workspace in eclimrc files and start eclimd with the -f or –file argument:
$ vim ~/.eclimrc1 osgi.instance.area.default=@user.home/workspace1 nailgun.server.port=9091 $ vim ~/.eclimrc2 osgi.instance.area.default=@user.home/workspace2 nailgun.server.port=9092 $ eclimd -f ~/.eclimrc1 $ eclimd --file ~/.eclimrc2
Note
The -f/–file argument is not supported by eclipse so the above option is only available when using a headless eclimd instance.
Hosting third party nailgun apps in eclimd¶
Since nailgun provides a simple way to alleviate the startup cost of the jvm, other projects utilize it as well. However, running several nailgun servers isn’t ideal, so eclim supports hosting other nailgun apps via an ext dir where you can drop in jar files which will be made available to eclim’s nailgun server.
The ext dir that eclim reads from is located in your vim files directory:
~/.eclim/resources/ext
